| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
- Kaggle
- R
- 실기
- 카카오
- Numpy
- level 1
- 코딩테스트
- python3
- pandas
- oracle
- 빅데이터 분석 기사
- seaborn
- level 2
- Python
- 머신러닝
- Oracel
- 튜닝
- SQL
- 프로그래머스
- 실습
- 파이썬
- 오라클
- 알고리즘
- sklearn
- matplotlib
- 데이터 분석
- 빅분기
- Today
- Total
라일락 꽃이 피는 날
[빅분기 실기] 랜덤 포레스트 (Random Forest) 본문
랜덤 포레스트 (Random Forest)
학습 데이터로 여러 의사결정나무를 구성하여 분석하고, 이를 종합하는 앙상블 기법
학습 데이터를 무작위로 샘플링해서 다수의 의사결정 트리를 분석하기 때문에 랜덤 포레스트라고 한다.
① 데이터에서 부트 스트래핑 과정을 통해 N개의 샘플링 데이터 셋 생성
② 각 데이터 셋에서 임의의 변수를 선택 - 총 M개의 변수들 중 sqrt(M) 또는 M/3 개
③ 의사결정트리들을 종합하여 앙상블 모델을 만들고 OOB error로 오분류율 평가
[주요 하이퍼파라미터]
- n_estimators : 나무의 수 (default = 100)
- max_features : 선택 변수의 수 ex) auto/sqrt, log2, none
Part 1. 분류 (Classification)
1. 분석 데이터 준비
import pandas as pd
# 유방암 예측 분류 데이터
data1=pd.read_csv('breast-cancer-wisconsin.csv', encoding='utf-8')
X=data1[data1.columns[1:10]]
y=data1[["Class"]]
1-2. train-test 데이터셋 나누기
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test=train_test_split(X, y, stratify=y, random_state=42)
1-3. Min-Max 정규화
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
scaler=MinMaxScaler()
scaler.fit(X_train)
X_scaled_train=scaler.transform(X_train)
X_scaled_test=scaler.transform(X_test)
2. 기본모델 적용
2-1. 훈련 데이터
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
model=RandomForestClassifier()
model.fit(X_scaled_train, y_train)
pred_train=model.predict(X_scaled_train)
model.score(X_scaled_train, y_train) # 1.0
① 오차행렬 (confusion matrix)
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
confusion_train=confusion_matrix(y_train, pred_train)
print("훈련데이터 오차행렬:\n", confusion_train)
정상 333명, 환자 179명을 정확하게 분류해냈다.
② 분류예측 레포트 (classification report)
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
cfreport_train=classification_report(y_train, pred_train)
print("분류예측 레포트:\n", cfreport_train)
정밀도(precision) = 1.0, 재현율(recall) = 1.0
2-2. 테스트 데이터
pred_test=model.predict(X_scaled_test)
model.score(X_scaled_test, y_test) # 0.9649122807017544
① 오차행렬 (confusion matrix)
confusion_test=confusion_matrix(y_test, pred_test)
print("테스트데이터 오차행렬:\n", confusion_test)
정상(0) 중 5명이 오분류, 환자(1) 중 1명이 오분류되었다.
② 분류예측 레포트 (classification report)
cfreport_test=classification_report(y_test, pred_test)
print("분류예측 레포트:\n", cfreport_test)
정밀도(precision) = 0.96, 재현율(recall) = 0.97
3. 하이퍼파라미터 튜닝
3-1. Grid Search
param_grid={'n_estimators': range(100, 1000, 100),
'max_features': ['auto', 'sqrt', 'log2']}n_estimators 값을 100에서 1,000까지 100개씩 증가하여 모델 튜닝을 설정한다.
max_features 값은 세 가지 방법 모두 설정한다. 그러나 auto와 sqrt는 동일한 방법이다.
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
grid_search=GridSearchCV(RandomForestClassifier(), param_grid, cv=5)
grid_search.fit(X_scaled_train, y_train)
print("Best Parameter: {}".format(grid_search.best_params_))
print("Best Score: {:.4f}".format(grid_search.best_score_))
print("TestSet Score: {:.4f}".format(grid_search.score(X_scaled_test, y_test)))
최적의 max_features는 auto, n_estimators는 100으로,
이때 훈련 데이터의 정확도는 97.7%, 테스트 데이터의 정확도는 96.5% 이다.
3-2. Random Search
from scipy.stats import randint
param_distribs = {'n_estimators': randint(low=100, high=1000),
'max_features': ['auto', 'sqrt', 'log2']}랜덤 탐색을 위해 n_estimators를 100~1000 사이의 범위에서, max_features는 세 가지 방법 사이에서
무작위로 20개의 모델(n_iter)을 분석하라고 설정한다.
from sklearn.model_selection import RandomizedSearchCV
random_search=RandomizedSearchCV(RandomForestClassifier(),
param_distributions=param_distribs, n_iter=20, cv=5)
random_search.fit(X_scaled_train, y_train)
print("Best Parameter: {}".format(random_search.best_params_))
print("Best Score: {:.4f}".format(random_search.best_score_))
print("TestSet Score: {:.4f}".format(random_search.score(X_scaled_test, y_test)))
최적의 max_features는 sqrt, n_estimators는 441로,
이때 훈련 데이터의 정확도는 97.5%, 테스트 데이터의 정확도는 96.5% 이다.
Part 2. 회귀 (Regression)
1. 분석 데이터 준비
# 주택 가격 데이터
data2=pd.read_csv('house_price.csv', encoding='utf-8')
X=data2[data2.columns[1:5]]
y=data2[["house_value"]]
1-2. train-test 데이터셋 나누기
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test=train_test_split(X, y, random_state=42)
1-3. Min-Max 정규화
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
scaler=MinMaxScaler()
scaler.fit(X_train)
X_scaled_train=scaler.transform(X_train)
X_scaled_test=scaler.transform(X_test)
2. 기본모델 적용
2-1. 훈련 데이터
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
model=RandomForestRegressor()
model.fit(X_scaled_train, y_train)
pred_train=model.predict(X_scaled_train)
model.score(X_scaled_train, y_train) # 0.9382384580348281
2-2. 테스트 데이터
pred_test=model.predict(X_scaled_test)
model.score(X_scaled_test, y_test) # 0.5832046084465448
① RMSE (Root Mean Squared Error)
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
MSE_train = mean_squared_error(y_train, pred_train)
MSE_test = mean_squared_error(y_test, pred_test)
print("훈련 데이터 RMSE:", np.sqrt(MSE_train))
print("테스트 데이터 RMSE:", np.sqrt(MSE_test))
3. 하이퍼파라미터 튜닝
3-1. Grid Search
param_grid={'n_estimators': range(100, 500, 100),
'max_features': ['auto', 'sqrt', 'log2']}n_estimators 값을 100에서 500까지 100개씩 증가하여 모델 튜닝을 설정한다.
max_features 값은 세 가지 방법 모두 설정한다. 그러나 auto와 sqrt는 동일한 방법이다.
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
grid_search=GridSearchCV(RandomForestRegressor(), param_grid, cv=5)
grid_search.fit(X_scaled_train, y_train)
print("Best Parameter: {}".format(grid_search.best_params_))
print("Best Score: {:.4f}".format(grid_search.best_score_))
print("TestSet Score: {:.4f}".format(grid_search.score(X_scaled_test, y_test)))
최적의 max_features는 log2, n_estimators는 300으로,
이때 훈련 데이터의 정확도는 56.9%, 테스트 데이터의 정확도는 59.3% 이다.
3-2. Random Search
from scipy.stats import randint
param_distribs = {'n_estimators': randint(low=100, high=500),
'max_features': ['auto', 'sqrt', 'log2']}랜덤 탐색을 위해 n_estimators를 100~500 사이의 범위에서, max_features는 세 가지 방법 사이에서
무작위로 20개의 모델(n_iter)을 분석하라고 설정한다.
from sklearn.model_selection import RandomizedSearchCV
random_search=RandomizedSearchCV(RandomForestRegressor(),
param_distributions=param_distribs, n_iter=20, cv=5)
random_search.fit(X_scaled_train, y_train)
print("Best Parameter: {}".format(random_search.best_params_))
print("Best Score: {:.4f}".format(random_search.best_score_))
print("TestSet Score: {:.4f}".format(random_search.score(X_scaled_test, y_test)))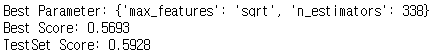
최적의 max_features는 sqrt, n_estimators는 338로,
이때 훈련 데이터의 정확도는 56.9%, 테스트 데이터의 정확도는 59.3% 이다.
'데이터 분석 > 빅데이터 분석 기사' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [빅분기 실기] 앙상블 배깅 (Bagging) (0) | 2022.06.19 |
|---|---|
| [빅분기 실기] 투표기반 앙상블 (Voting Ensemble) (0) | 2022.06.19 |
| [빅분기 실기] 의사결정나무 (Decision Tree) (0) | 2022.06.18 |
| [빅분기 실기] 서포트 벡터머신 (SVM) (0) | 2022.06.18 |
| [빅분기 실기] 인공신경망 (0) | 2022.06.17 |
